Acquisition of Knowledge and Construction of Learning Settings According to Student Cognition in Constructive Teaching İETC-2015
Sevinc Abbasova
Fatma khanim Bunyatova
 This study explores how students gain and build their knowledge through lessons conducted in constructive teaching settings and advantages of self-assessment students carried out.
This study explores how students gain and build their knowledge through lessons conducted in constructive teaching settings and advantages of self-assessment students carried out.
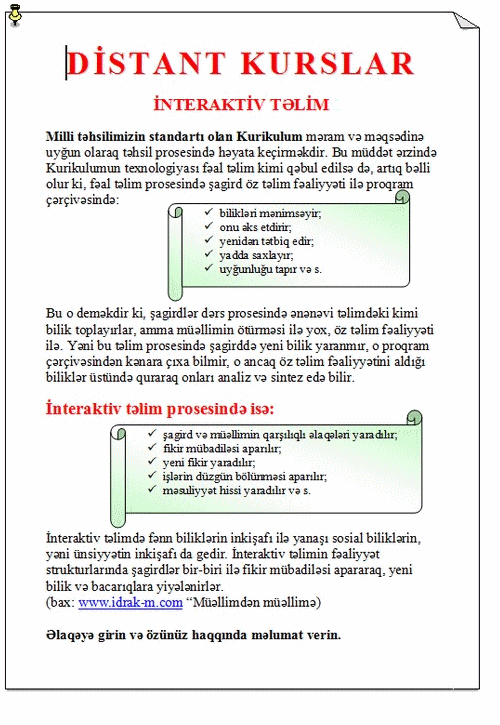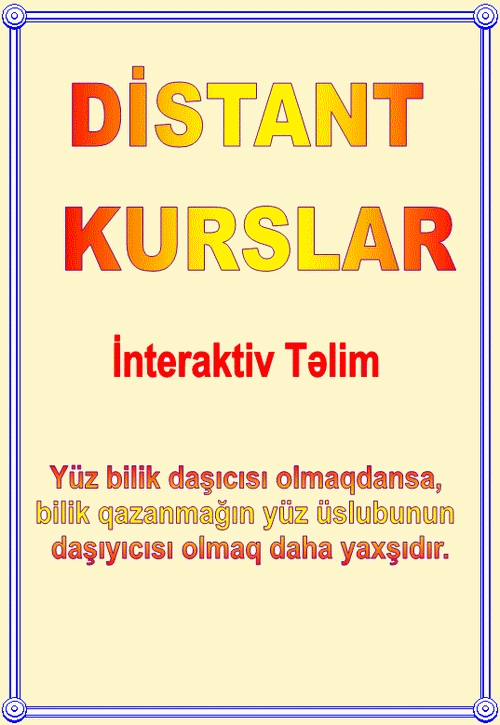
In the recent years, there has been intensive integration process taking place in educational system of Azerbaijan, with numbers of educatinal reforms. Getting approval of the national curriculum, implementation of science curricula has begun. Interactive teaching was chosen as a main educational strategy of the reforms and at the present teachers of all sciences try to establish their pedagogical activities in this direction.
Throughout the active courses, students are active and work hard. They gain a knowledge and have discussion about it, afterwards. Several methods are made use of in this approach to enhance the students activity, which, however, takes place under the guidance of the teacher only. In other words, under the direction of teacher, students do adopt the knowledge, which was the preliminary purpose of the traditional teaching, where the teacher was herself seeking for best ways to deliver the knowledge to students.
The principles of acquisition of knowledge as a knowledge assimilation, and making little amends on the received knowledge, and properly doing the given assessments are for forming a particular type of thinking, and commitment, but not creavite thinking. Making a creative thinking is to build up student’s his or her own ideas, making use of self thinking via the learning methods.
To achieve this goal and let students construct their own ideas, particular Geography module, based on the principles of constructive teaching methods, was introduced to students. Bringing out students’ intuitive, precise and formal knowledge about the subject, built simple matter of the fact among students, which later kept intensively developing as each idea generated by students broadaned the knowledge by refreshing and updating itself each time. In the following stages, teacher took the position of transforming the explored pre-knowledge into scientific knowledge and form, followed by assesments given to students to strengthen and stabilize the knowledge in the memory. At the end of the lesson, tasks given to students to perform in the assessments, let to reveal out the constructed knowledge and analyze it, which were outcome of several logical operations.
Comparing both teaching methods – constructive and active — , the differences observed in the following cases:
—Structure of the questions: The key questions used in interactive teaching to pose the knowledge are “What is it?”, “Where it is?” and “When? “.
Whereas, in constructive teaching, queastions are grounded in to reveal out the meaning of the knowledge. These questins are as “How do you understand this?”, “ What does it tell you?”, “How to make changes on it?”. Make use of such constructive and thought-provoking questions disclosed students visions, ways they utilized for thinking, and skills they had acquired. In addition, this questions led each student express and share their skills and knowledge between each other, update their knowledge and perform a self assessment on their knowledge and ability they own.
-Leading the lesson: As teacher is in the primary position of guiding and delivering the knowledge through out the lesson, there occur relatively less teamwork in active teaching settings and thus students are rather more passive learner. However, interactivity is more focused at in lessons constructive teaching environment.
-Discussions: Significant difference occured by the time it came to discussion. There made only three and four discussion during the lesson conducted in active teaching settings, where as we ended up with nearly 30 questions discussed in students in groups and then whole class.
During this discussions, each student creates his or her new knowledge by integrating it with pre-existing knowledge , as well as learn the ways of assimilation of knowledge and develop ability of thinking and social skills.
Baxış: 1110